Australasia, Melanesia, Micronesia, and Polynesia are all part of Oceania. Oceania is a continent that spans the Eastern and Western Hemispheres. Its surface area is 8,525,989 square kilometres (3,291,903 square miles) with a population of over 41 million people. Oceania is the smallest continent in terms of land area and population after Antarctica.
 Pacific Islanders, Pacifier, Pasifika, or Pasefikaare ethnic/racial words used to define the Pacific islands indigenous people. They are the inhabitants and diaspora of any of Oceania's three primary sub-regions (Melanesia, Micronesia, and Polynesia). The phrase "Pacific Islander" is unique from referring to the indigenous peoples of Oceania since it can apply to both indigenous and non-indigenous peoples of the Pacific Islands, as well as Aboriginal Australians.
Pacific Islanders, Pacifier, Pasifika, or Pasefikaare ethnic/racial words used to define the Pacific islands indigenous people. They are the inhabitants and diaspora of any of Oceania's three primary sub-regions (Melanesia, Micronesia, and Polynesia). The phrase "Pacific Islander" is unique from referring to the indigenous peoples of Oceania since it can apply to both indigenous and non-indigenous peoples of the Pacific Islands, as well as Aboriginal Australians.
A.Australia(Aboriginal Languages)
The estimate of indigenous languages spoken in Australia is in the hundreds. They are about 250 to 363 in number. Australia's Indigenous languages are made up of about 13 language families and isolates. These language families are spoken by Indigenous peoples on mainland Australia and a few surrounding islands. The links between the language families are currently unclear, while there are plans to combine some of them into bigger groups. Despite this ambiguity, the Indigenous Australian languages are commonly referred to as Australian languages or Australian families in technical terms.10 most spoken Aboriginal languages
- Ammatyerre – Central Australia, Northern Territory
- Anindilyakwa – Groote Eylandt, Northern Territory
- Arrernte – Central Australia, Northern Territory
- Djambarrpuyngu – Arnhem Land, Northern Territory
- Luritja – Western Desert, Central Australia
- Murrinh-Patha – Wadeye, Northern Territory
- Pitjantjatjara – AnanguPitjantjatjaraYankunytjatjara (APY Lands), Central Australia
- Tiwi – Tiwi Islands, Northern Territory
- Warlpiri – Central West, Northern Territory
- WikMungkan – Aurukun, Cape York, QLD
B.Pacific Islands Indigenous(Micronesia,Melanesia,Polynesia)
 Pacific Islanders, Pacifier, Pasifika, or Pasefikaare ethnic/racial words used to define the Pacific islands indigenous people. They are the inhabitants and diaspora of any of Oceania's three primary sub-regions (Melanesia, Micronesia, and Polynesia). The phrase "Pacific Islander" is unique from referring to the indigenous peoples of Oceania since it can apply to both indigenous and non-indigenous peoples of the Pacific Islands, as well as Aboriginal Australians.
Pacific Islanders, Pacifier, Pasifika, or Pasefikaare ethnic/racial words used to define the Pacific islands indigenous people. They are the inhabitants and diaspora of any of Oceania's three primary sub-regions (Melanesia, Micronesia, and Polynesia). The phrase "Pacific Islander" is unique from referring to the indigenous peoples of Oceania since it can apply to both indigenous and non-indigenous peoples of the Pacific Islands, as well as Aboriginal Australians.
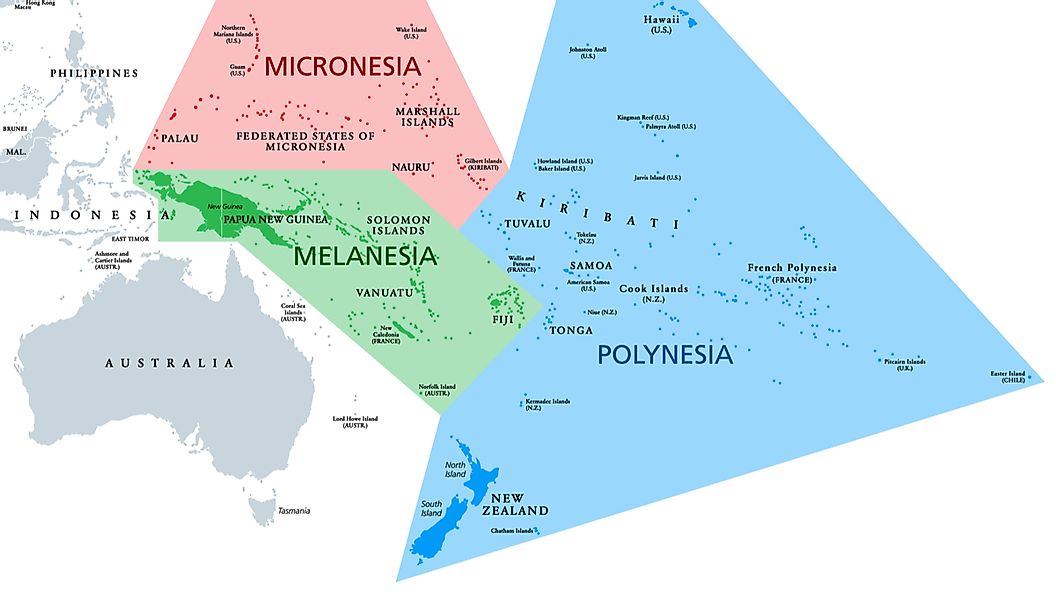
Melanesia
Melanesia is the large arc of islands in the north and east of Australia, south of the Equator. The name comes from the Greek words melas ('black') and nsos ('island'). The residents of this sub-region are mostly the dark-skinned peoples of New Guinea island, the Bismarck Archipelago, Solomon Islands, Vanuatu (previously New Hebrides), New Caledonia, and Fiji. Melanesia also includes the Admiralty Islands, Bougainville Island, Papua New Guinea, Western New Guinea (part of Indonesia), Maluku Island, Aru Islands, Kei Islands, Santa Cruz Islands (part of the Solomon Islands), Loyalty Islands (part of New Caledonia), Norfolk Island, and various smaller islands.Micronesia
Kiribati, Nauru, the Mariana Islands (Guam and the Commonwealth of the Northern Mariana Islands), the Marshall Islands, Palau, and the Federated States of Micronesia are all part of Micronesia (Yap, Chuuk, Pohnpei, and Kosrae, all in the Caroline Islands).Polynesia
The Polynesian islands are strewn across a triangle in the Pacific Ocean's east-central area. The Hawaiian Islands are to the north, New Zealand is to the west, and Easter Island is to the east. The Cook Islands; French Polynesia (the Society Islands [Tahiti], Marquesas Islands, Austral Islands, and Tuamotu); Niue Island; Tokelau and Tuvalu; Tonga; Wallis and Futuna; Rotuma Island; Pitcairn Island; Nukuoro; and Kapingamarangi make up the remainder of Polynesia.Some of the most spoken Pacific islands languages
- Burmese
- Cantonese
- Chinese
- Formosan
- Hmong
- Indonesian
- Micronesian
- Mien
- Trukese
- Uighur
